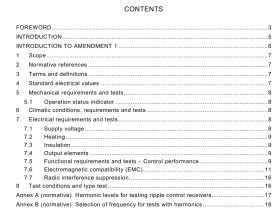
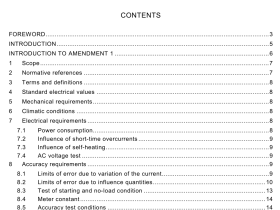
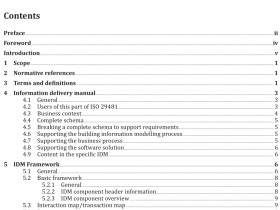
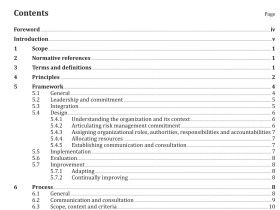
AS 3515.3 pdf download

AS 3515.3 pdf download.Gold and gold bearing alloys
3 Definitions
For the purpose of this Standard, the definitions below apply. 3.1 bullion an alloy of gold and silver with variable amounts of one or more of the base metals 3.2 cornet an alloy of gold and silver after it has been hammered, annealed and fashioned into a roll, prior to parting 3.3 cupellation the process by which the precious metals are separated from the lead and other base metals with which they are alloyed. It is also the process whereby the sample, having been wrapped in lead sheet/foil with the necessary additives (i.e. silver and copper), is homogenized in the molten state prior to the separation of the gold and silver 3.4 fine gold of purity greater than 99.5 % gold 3.5 gold cornet a cornet that has been parted 3.6 laboratory sample a sample as prepared for sending to the laboratory and intended for inspection or testing 3.7 may indicates the existence of an option 3.8 parting the separation of gold from other precious metals by means of nitric acid in a chloride-free environment, where the silver forms soluble silver nitrate and the gold remains undissolved 3.9 prill the “button” or “bead” of precious metal obtained from the cupellation process 3.10 proof a reference sample included in each batch of samples in order to monitor the effect of assay conditions 3.11 reference standard a reference material included in each batch of samples to determine the accuracy of the analysis 3.12 shall indicates that a statement is mandatory 3.13 should indicates a recommendation 3.14 surcharge the sum of the gains and losses of mass of the proofs during the assay process, determined as a mean value Note 1 to entry: Negative surcharges are not acceptable in fine gold analysis. 3.15 test portion the portion of material taken from the test sample or, if both are the same, from the laboratory sample, on which the test or assay is actually carried out 3.16 test sample a sample prepared from the laboratory sample and from which test portions will be taken
4 Principle
An accurately weighed test portion is cupelled. The resultant prill is hammered, cleaned, rolled and then parted in nitric acid. The resultant gold cornet is washed, dried, annealed and weighed.
5 Reagents
Analytical grade reagents (AR) shall be used. Deionized or glass distilled water of Grade 3 as defined in ISO 3696 shall be used. The following reagents shall be used for the test method in this Standard: (a) Nitric acid (ρ 20 1.42 g/mL). Nitric acid shall be of AR purity, and shall not contain chloride ion at a concentration in excess of 1 mg of chloride per litre. (b) Nitric acid (1:2). A solution prepared by cautiously adding one volume of nitric acid [see Clause 5(a)] to two volumes of water, while stirring continuously. (c) Nitric acid (1:1). A solution prepared by cautiously adding one volume of nitric acid [see Clause 5(a)] to one volume of water, while stirring continuously. (d) Silver. Containing at least 99.9 % silver (Ag) and less than 5 mg of gold (Au) per kg of silver. (e) Proof gold. Containing at least 99.9965 % gold with a previously determined accurate value. (f) Copper metal – AR Grade. (g) Assay grade lead foil. (h) Acetone AR grade > 99.5 %.
6 Apparatus
Where possible, equipment dedicated to the analysis of fine gold should be used. CAUTION — CLEAN THE EQUIPMENT WITH METICULOUS CARE TO AVOID CONTAMINATION. The apparatus shall be as follows: (a) Magnesite cupels. Suitable for up to 7 g of lead. NOTE Magnesite cupel blocks of similar lead absorption capacity are suitable. (b) Anvil and hammer. Of polished steel. (c) Micro-analytical balance. Capable of a resolution of 0.001 mg. (d) Annealing furnace. Capable of attaining and maintaining a temperature of 800 ± 50 °C. (e) Cupellation furnace. Capable of attaining and maintaining a controlled oxidizing atmosphere and a uniform temperature of 1050 ± 20 °C.