AS ISO 7451 pdf download

AS ISO 7451 pdf download.Earth-moving machinery — Volumetric ratings for hoe- type and grab-type buckets of hydraulic excavators and backhoe loaders
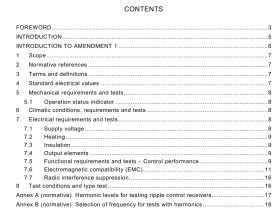
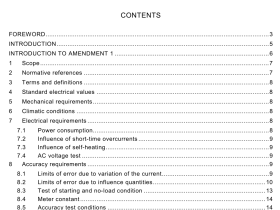
1 Scope
This International Standard specifies a method for estimating the volume of materials which a hoe- type or grab-type bucket of a hydraulic excavator or backhoe loader can normally contain. The volume assessments are based on the internal dimensions of the bucket and on the representative volumes at the top of the bucket. The method employs the technique of dividing the complex shape of the material in the bucket into simple geometric shapes. This method of assessment is intended to provide a conventional means of comparing bucket capacities. It is not intended to be used to define true capacities. This International Standard is not applicable to buckets of cable excavators.
2 Terms and definitions
For the purposes of this document, the following terms and definitions apply. 2.1 hydraulic excavator self-propelled machine on crawlers, wheels or legs, having an upper structure capable of a 360° swing with mounted equipment and which is primarily designed for excavating with a bucket, without movement of the undercarriage during the work cycle Note 1 to entry: An excavator work cycle normally comprises excavating, elevating, swinging and discharging of material. Note 2 to entry: An excavator can also be used for object or material handling/transportation. Note 3 to entry: For hoe-type bucket components (see Figure 2). Note 4 to entry: Adapted from ISO 6165:2006. 2.2 backhoe loader self-propelled crawler or wheeled machine having a main frame designed to carry both front-mounted equipment and rear-mounted backhoe equipment (normally with outriggers or stabilizers) Note 1 to entry: When used in the backhoe mode, the machine is stationary and normally digs below ground level. Note 2 to entry: When used in the loader mode (bucket use), the machine loads through forward motion. Note 3 to entry: A backhoe work cycle normally comprises excavating, elevating, swinging and discharging of material. 2.4 Y dimension Y maximum depth of the indentation, perpendicular to the strike plane, on a hoe-type bucket (see Figure 4) 2.5 strike plane 〈hoe-type bucket〉 horizontal plane extending over the width of the bucket from the cutting edge or face of the leading edge to the contact edge between the horizontal plane and the backsheet (see Figure 3) 2.6 strike plane 〈grab-type bucket〉 horizontal plane extending over the width of the bucket and passing through the top edges of the backbands (see Figure 12) 2.7 strike surface cylindrical surface of radius R on the hoe-type bucket, which traverses the edges of the strike plane (face of the leading edge and contact edge of the backsheet) and which is tangential to a plane parallel to the strike plane and at a distance Y (see Figure 4) 2.8 surface area S 1 area of a hoe-type bucket’s side internal surface bordered by the strike plane (see Figure 8) 2.9 surface area S 2 area of a hoe-type bucket’s side internal surface bordered by the strike surface (see Figure 9) 2.10 surface area S 3 area of a grab-type bucket’s side internal surface bordered by the strike plane (see Figure 12) 2.11 surface area S 4 area of a grab-type bucket’s side internal surface used for calculating top volume (see Figure 13) 2.12 struck volume V s volume lying beneath the strike plane or the strike surface 2.13 top volume V t volume of material situated above the strike plane 2.14 displaced volume V m volume of material inside the grab-type bucket displaced by the operating mechanism or structure 2.15 volumetric rating V r volume determined by the method detailed in this International Standard, providing a means of comparing the capacities of buckets2.16 W dimension W internal width at the barycentre of the bucket section (see Figures 8 and 9) 2.17 W 4 dimension W 4 mean between the inside width of the backsheet level with the edge in contact with the strike plane and the inside width of the leading edge increased by twice the thickness of the sides (see Figures 10 and 11)